Under U.S. law, all healthcare providers, institutions, and their associates who deal with protected health information (PHI) must follow predefined guidelines under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This obligation ensures the careful handling and protection of sensitive patient information.
To perform a safe and trusted practice, every organization in the Healthcare industry must be aware and up-to-date with the rules that allow them to be known as ‘HIPAA Compliant.’ Let’s walk through all the aspects related to HIPAA and the security of patient data to ensure that you tick all the boxes of the HIPAA-Compliant Checklist.
What is HIPAA Compliance?
HIPAA Compliance refers to the process of organizations abiding by certain security and privacy rules that guarantee trust and integrity from the healthcare institution’s end while handling patient data. Everyone who has access to any protected health information—hospitals, insurance companies, business associates such as healthcare law firms, and IT departments—have to comply with the regulations set by HIPAA.
Losing, tampering with, or misusing a patient’s delicate information is highly unethical and goes against the law. Any entity violating HIPAA Compliance faces legal action or pays heavy penalties after undergoing a thorough investigation by the HHS Office for Civil Rights or the Federal Trade Commission.
If you want to steer clear of such costly affairs and retain the respect of your patients or customers, you should go the extra mile in understanding what to do to be fully HIPAA Compliant!
The 12 Rules HIPAA Compliant Checklist to Follow in 2024
The HIPAA Compliance Checklist is a valuable resource that entities and business associates use to guide them toward complying with the necessary policies and practices of working with PHI and e-PHI. It also helps introduce better preventive measures and bridge operational gaps in the institution.
Here is a 12 Rules Checklist that you can refer to and implement in your daily practices in order to achieve HIPAA Compliance:
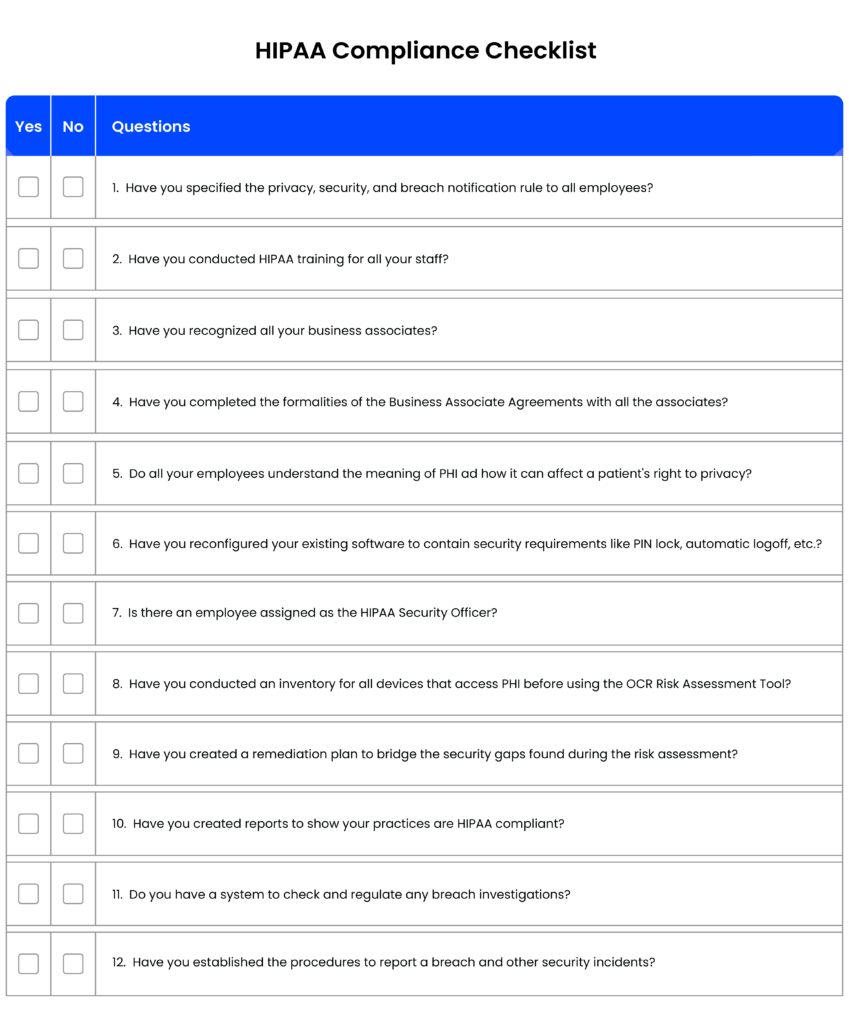
[You can also download the checklist to share it with your team: 12 Rule HIPAA Compliant Checklist]
We know that a checklist might not be enough to understand the broader concept of these rules. So, let’s check out the best HIPAA-compliant practices that will assist you to get a better picture.
1. Clarity with HIPAA’s rules
The first thing to become a HIPAA-compliant entity is to be aware of the following rules:
The Privacy & Security Rule defines the administrative regulations that aim to promote better health information systems by establishing standards and requirements for managing PHI and electronic PHI.
While the Health and Human Services Department provides a detailed procedure that an organization must follow in case of a breach of unsecured health information.
If you are well-versed in the HIPAA rules, their need, and value, you will have an easier time following them and incorporating them into your day-to-day activities.
2. Understand your part
As discussed, HIPAA lays out several rules for protecting healthcare data, but the laws differ for covered entities and business associates. Hence, knowing where and how you play a role is crucial.
Covered entities like health plans, healthcare providers, and healthcare clearing houses are organizations that manage PHI data for their customers or patients. On the other hand, business associates are entities that offer their services to the covered entities and also have access to e-PHI.
The Security and Breach Notification Rules are the same for covered entities and business associates. However, Privacy Rules and Administrative Requirements consider the service offered by the business associates and the set conditions of the Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
3. Identify sensitive data
Any institution receives a massive amount of data every day. However, only a minor part requires security measures.
According to HIPAA, protected health information is individually identifiable information related to a customer or patient’s past, present, and future mental and physical health or payment transactions.
PHI includes social security numbers, contact details, fingerprints, and other private data. It’s essential to determine the information your organization deals with and check the areas where protected information is present. Doing so can help you align processes while handling the data and enable appropriate security measures like passwords or encryptions.
4. Avoid data breaches
From failing to perform a risk analysis to inappropriately disposing of PHI, an organization can commit a HIPAA violation in numerous ways. Even if it’s unintentional, there can be an investigation and a hefty fine to pay in its wake. So, the organization should prepare for any plausible system breach.
You can do this by conducting a risk analysis regularly using the OCR’s Security Risk Assessment Tool, which abides by all of HIPAA’s policies. It can assist with discovering gaps with respect to the updated rules and problems in old software.
5. Assign responsibilities
For a system to work smoothly, the people involved must know their part in the process. Guide your workforce on HIPAA’s compliance obligations and outline the practices they must adopt in all their activities.
Entrust the onus and accountability to teams dealing with monitoring, auditing, and training for HIPAA compliance. Assigning responsibility will help every team keep the other in check and avoid potential violations.
6. Ensure your tools and software are HIPAA compliant
HIPAA-compliant tools and software enable institutions to follow the pre-set rules and regulations of HIPAA in their numerous medical practices. With the use of such software, all entities and their associates can achieve the following:
- Save Time and Effort: HIPAA-Compliant software tracks any movement of devices and media available at a glance.
- Enhance Security: Good tools and software guarantee better protection of e-PHI by introducing features such as PIN-locked access and automatic logoff to safeguard from unauthorized entry.
- Increase Patient Trust: Using HIPAA-compliant tools and software shows you take all necessary precautions to protect their privacy. It fosters trust between both parties and, in time, leads to more patient acquisition.
7. Be on top of all changes
HIPAA’s rules and policies update with the changing times. The list is renewed yearly to safeguard the patients’ data better and address the necessary loopholes. Covered entities and business associates must understand all the changes for a breach-free work environment.
The new list also allows one to re-evaluate security measures, train users and address gaps.
8. Keep track using documentation
After understanding the rules, training your workforce, and implementing necessary measures, you should check all the developments and improvements by documenting them.
You can employ HIPAA compliance software to record this information which may include the organizations you share PHI or e-PHI with, various versions of the laws and policies, and any potential breaches.
9. Report violations immediately
In the event of a security breach, the organization must inform the Secretary of Health and Human Services within 60 days, as well as the people whose sensitive data was compromised.
The Breach Notification Rule specifies the process the organization must go through and whom they must notify in their respective situation. A thorough investigation by the Office of Civil Rights follows the reporting of the incident.
Best Practices to be in HIPAA’s good books
Do you remember every rule in the numerous papers your H.R. asked you to sign at the beginning of your job? Probably, not. However, you are well aware of the day-to-day practices that help you avoid any breach of trust.
Most of us share this tendency as it’s easy to adopt simple habits than cramming up complicated rules. While you can conduct frequent audits to ensure HIPAA compliance, there are a few best practices that your healthcare facility can follow to stay on track with the compliance guidelines.
- Lay out clear standards: You must provide your staff with intelligible, accessible, and specific instructions to handle protected health information and maintain cybersecurity.
- Conduct HIPAA training: A 2018 Ponemon Institute report said that staff negligence is responsible for about 65% of security violations. Hence, the workforce in contact with PHI and e-PHI must undergo HIPAA training to manage sensitive information appropriately. You can opt for government-sponsored HIPAA compliance training for your staff or access free resources for caregivers from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Strict follow-through: Once the staff completes the training and understands the set policies and procedures, you should ensure they adopt every small practice, like using strong passwords, encrypting the PHI, and not giving access to unauthorized people.
- Determining potential risks: Every entity dealing with PHI has some different rules and regulations under HIPAA. They can undergo annual risk assessments to confirm that everyone is doing their part correctly. This process helps you identify gaps and develop new strategies and policies to become HIPAA compliant. In the event of an unexpected breach, handle all the plausible gaps in the system that led to it and enable new measures to avoid it in the future.
Now that we know these steps to become HIPAA compliant, we are just a few steps away from passing the audit with flying colors!
How to Ace HIPAA Compliance Audits?
The HIPAA audit typically consists of an assessment of administrative, physical, and technical securities governing the protected health information of an organization. It also investigates the organization’s policies and procedures in managing sensitive data and the workforce’s preparedness during an unsuspected violation.
It might seem anxiety-inducing, but even the dreadful words ‘Test Day’ make the slightest difference to a well-prepared mind.
The HIPAA Journal provides an audit checklist for covered entities and business associates that elaborately outlines the required compliance obligations. For your organization to ace the audit, the following information must be at your fingertips:
- What makes up PHI and e-PHI
- People with special access
- Results of workforce training for HIPAA
- Standard security practices described by NIST or SANS
- Location of PHI in the network
- Procedure during a violation of the rules
You must be curious—what if I still fail the audit?
If an organization fails the HIPAA Compliance Audit, it will undergo a restrategizing planning phase with the Office of Civil Rights (OCR) to adopt new policies and become HIPAA Compliant. The corrective measures can become very thorough, from training the staff and developing better policies to a complete data risk analysis. In some cases, the OCR will penalize the organization based on the four tiers that examine the severity and time period of the violation.
However, if you follow the checklist of 2024 and work with efficient HIPAA-compliant software, you are bound to ace the audit!
I hope you found this checklist helpful, and it helps you make your practice a 100% HIPAA-Compliant.
If you are looking for a HIPAA-Compliant CRM that easily integrates with many EHR solutions, look no further than LeadSquared CRM. It promises to protect the patient’s privacy in all its medical practices while simplifying and managing your staff’s daily activities.
FAQs
Medical records, lab results, and hospital bills are some examples that fall under the category of PHI since they all include the patient’s identity and other identifiable information linked to their health.
According to the HHS site, the Office for Civil Rights is responsible for enforcing the HIPAA privacy and security rules.
When an entity commits a Tier 4 violation (where the negligence had been intentional and no corrective measures proceeded within 30 days), it can face the maximum penalty. The minimum fine per violation for Tier 4 violation is $50,000 and can reach a maximum of $1,919,173.









