The customer data analysis capabilities of a business determine its success. Understanding the customer at a personal level can help shape effective business strategies. This knowledge can help improve customer service, improve marketing communication, and create better brand value. Managing customer data efficiently can also help improve return on investment.
Today, collecting consumer data is inexpensive and effortless. Data-driven solutions can segregate consumers based on their demographic details, interests, behavior, and other data that consumers share across different touchpoints. By using this information, businesses can position themselves as a consumer-centric brand. Brands can cater to their customers at a much more personal level if they can manage the customer data effectively. Hence, the need for customer data management or CDM.
What is customer data management?
Customer data management is a process of collecting, analyzing, and managing the data that the consumers have shared with the business. This data collection and analysis allows brands to solve customer’s specific issues while maintaining customer satisfaction levels. When a brand delivers real value to its consumers, it also increases the customer retention rate.
Insights from customer data (including the data they provide through form fills and other means and the data you capture via behavior tracking) gives brands in-depth customer intelligence (CI). CI is the collection and analysis of large amounts of data that determine the best and most effective ways to interact with customers. A CI-driven mindset presents the following benefits:
- Provides an overview of customer demands
- Increases sales efficiency and improves ROI
- Develops more reliable and sustainable customer relationships
- Delivers better customer experience that leads to customer loyalty
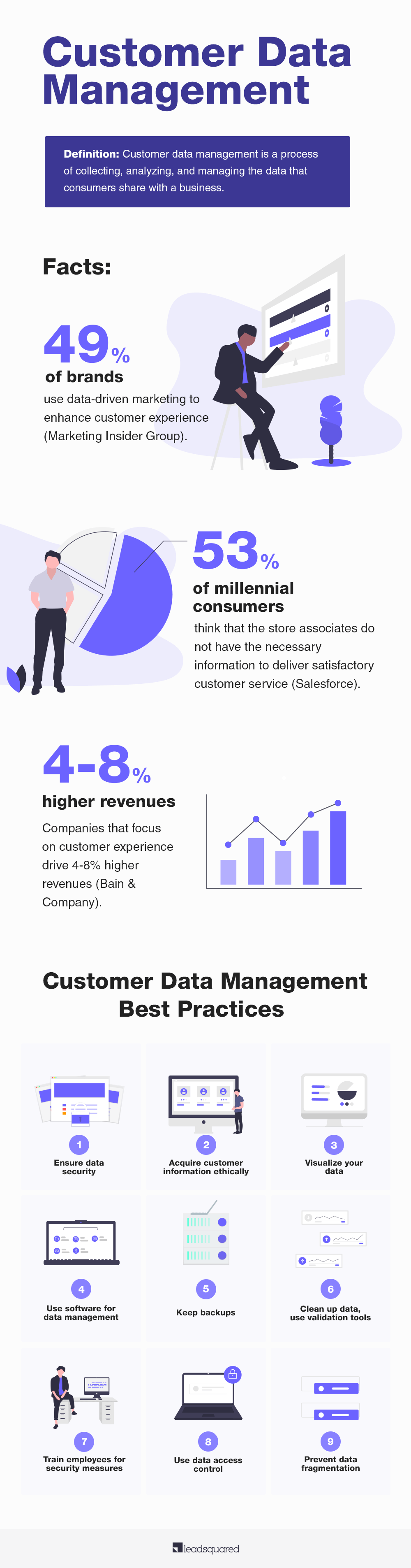
Brands now use customer data as much as possible to improve the experience. 49% of brands use data-driven marketing to build meaningful relationships and customer journeys. However, there still is room for improvement. For instance, 53% of millennial consumers think that the store associates do not have the necessary information to deliver satisfactory customer service. However, companies that focus on customer experience drive 4-8% higher revenues than their competitors.
If you see, there are two main aspects of customer data management:
- Customer data collection: it involves ethical data collection strategies.
- Customer data management: it deals with secure storage of customer data, authorized access, and data-driven analytical insights.
Let us dive into details.
Customer data collection strategies
Customer data collection can be of various types. Each data collection method has a specific purpose. For instance, you can use single-field forms on the top of web pages to attract top-of-the-funnel prospects. Forms that ask for detailed information can be used a little further down the funnel – when the sales intent seems higher. In any case, all data collection should be done ethically and with the consent of the user.
Before we discuss data collection strategies, a quick look into the types of customer data and the purpose they serve.
Types of customer data
There are four types of data that brands collect for their sales and marketing strategies.
- Identity data: This information allows brands to identify an individual and facilitate communication with them. It may include name, email address, phone number, date of birth, gender, location, address, social media profiles, name of the company, job profile, and more.
- Descriptive data: These are personal information such as marital status, number of kids, hobbies, travel history, and more that can help a brand get a fuller perspective of the customer.
- Quantitative data: These are operational data that define the interaction of a customer with your brand. It may include transactional data (products purchased, total money spent, date of purchase, abandoned carts), website visits, communication channels, and interaction data with sales/support teams.
- Qualitative data: These are usually the feedback and survey data that helps brands understand the customer perception and perform quality checks.
You can use different types of data to achieve specific goals. Also, the methods to collect these data will differ. In general, customer data collection methods involve:
- Top of the funnel data collection
- Bottom of the funnel data collection
Top of the funnel data collection
Top of the funnel customer data is low effort information. Examples of such data are email address, or the first name, or both.
Here, the amount of information that a person is willing to give will depend on the value the person perceives from the offer. For instance, people would be happy to share an email ID, but they would never like to share their company name, phone number, etc. for a blog subscription.
There are numerous ways to collect the top of funnel customer data. Embedded forms, gated content, landing pages, lead gen forms, and chatbots are some examples.
Once you have this data and the person’s consent for communication, you can nurture them to move them down the funnel. For instance, you can send them a webinar invite or send them an eBook. You can request them for further details (descriptive data) if they are willing to interact with you.
Brands that use CRM software can easily collect quantitative data such as the interaction history of a person. For instance, when a person accepts cookie policies, the software gets permission to track their interaction on the website and ads. This information is crucial for brands to understand the needs and the buying intent of the customer. Accordingly, they can recommend products/services or let a salesperson reach out to the consumer.
Middle of the funnel customer data collection
The middle of the funnel data collection relates to direct customer acquisition strategies. Here, the prospects may already be in the consideration phase of the sales funnel.
The type of content that can help here are case studies, whitepapers, demo videos, and ebooks that talk about industry use cases. You can use landing pages or pop-up forms to collect their details, such as industry, business email id, company name, and phone number.
Bottom of the funnel customer data collection
When a person shows a buying intent, then he/she is said to be at the bottom of the funnel. However, to make an effective sales pitch, you will still need more information from the person, such as industry and job profile.
In such cases, people are likely to share more information, such as phone number, company name, timings for the demo, etc. It is because they perceive more value in a product demonstration, and they are closer to buying. Often, people know that sharing this information would lead to a better/more customized demo.
The popular tools for capturing this data are:
- Landing pages
- Chatbots
- Free tools such as an insurance policy quote generator and website grader
- Social media lead generation forms (e.g., Facebook, LinkedIn forms) that pre-fetch customer information – making form filling easy.
- AI-powered widgets that automatically evaluates the product fitment based on your business requirements.
However, there is a fine line between the information you ask for and the information people are comfortable sharing with anyone. For example, people may not be willing to provide their credit card information for a trial. Here, the perceived value of the information they provide is greater than the perceived value of the benefits they get.
By understanding customer sentiments, you can apply them effectively for different types of data collection.
After customer acquisition, you can collect their feedback, take a product satisfaction survey, and utilize this data for quality control measures. However, you must ensure privacy and data security while collecting customer data.
Let us now move on to customer data management best practices.
Customer Data Management Best practices
Back in 2016, Uber suffered a data breach where hackers leaked details of 57 million users. This data also includes six hundred thousand driving license information. The settlement cost the company 148 million USD. Not only did this cost them money, but it also damaged the reputation of the company. Uber made it worse by trying to hide the breach from the public.
Data breaches devastate customers’ trust in the company. Consumers will eventually know that their private information is compromised. For example, Web browsers can now alert users. Websites like haveibeenpwned.com show how a customer’s data was leaked and from where.
Therefore, as a brand, customer data is your responsibility. Follow these best practices for effective customer data management.
1. Be serious about data security
Data breaches can be expensive. The average cost of a data breach is 3.86 million USD. Small and medium-sized businesses lose approximately 120,000 USD per data breach, on average (source: usa.kaspersky.com). So, brands must take all the necessary precautions to ensure that customer data is not compromised. Information such as email, names, addresses, and contact numbers are vulnerable to identity theft. So, when planning to take customer data, you must also plan to keep that information safe.
The first step in keeping your customer data safe is by investing in a secure CRM. Next, you also need to keep a backup system. Finally, you need to train your staff on how to handle customer data.
2. Acquire customer information ethically
Always ensure that the customer has agreed to share the data with you. Trust and transparency are essential in data collection. Allow the customers to opt-out of communications. Draft a privacy policy on your website and use straight-forward surveys while asking for information.
3. Do not collect redundant data
If you are trying to capture too much information when it’s not needed, you are probably losing the few details that you could have collected. For instance, a 10-field form for an e-book download is not needed.
Also, too much data can be useless. First, understand what data you will need and then collect the data. It will reduce a lot of overhead. Do not collect data simply because you can.
An alternative to this could be the lead deduplication feature of the CRM software. It identifies duplicate records and merges them to create a unique lead record. For example, if a visitor submits his details first on your website and then on lead gen ads, the system registers the latter as an activity record.
4. Invest in a software platform for data management
CRM platforms come with built-in databases for storing customer data. Separate, secure databases for customer data are also required to make your data-collection GDPR compliant.
5. Keep backups
Data loss is common in businesses. However, many companies (nearly 58% of small businesses) are not prepared to prevent such loss.
Data backup could be as simple as creating a copy regularly and systematically. Cloud-based CRMs take care of it automatically.
6. Clean up the data; use validation tools
Customer data management can be painful when there is a lot of junk. Data can also be outdated quickly in B2B scenarios. Data cleansing and validation ensure that you always have the updated data.
7. Train employees for security measures
Customer data management is a sensitive task. Your company staff should understand that when working with it. You need to enforce rules, particularly if your business has a BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policy.
8. Use data access control
An extension of the previous point is controlling access to customer data. CRM helps here in a big way by ensuring that only those needed have access to customer data. Access control makes customer data management effortless.
[Also read: the basics of cloud security]
9. Prevent data fragmentation
The inefficient use of storage space (in computer storage) leads to data fragmentation. It reduces the application’s storage capacity and performance.
Keeping your data clean and collecting only the required information is quintessential to preventing fragmentation.
10. Visualize your data
Data visualization is crucial to understanding the quality of your collected data. The collected data must be digestible visually. You can use this to gain unique insights or tell a story.
Conclusion
Today, businesses need customer data to excel in such a competitive landscape. However, customer data management is a sensitive task and can get messy if not done correctly. Tools such as CRM solves this issue. However, companies should also invest in training their employees. They should stay transparent about how they are using customer data.
Make your customer data management a no-sweat job.Check out LeadSquared’s HIPAA and GDPR compliant CRM software solution. Book a Demo!









