In the world of manufacturing, productivity and cost-efficiency are like gold dust. When your manufacturing processes are firing on all cylinders, you’re not only churning out products faster but also doing it with fewer resources. That means more profit in your pocket and room for growth.
In this article, we’ll delve into the nuts and bolts of streamlining your manufacturing workflows. We’ll discuss practical strategies that boost productivity and pave the path for growth. It’ll help you make smart choices for your manufacturing workflows, positively impact financials, and do more with less.
But before we start, let’s discuss what manufacturing workflows are.
What are manufacturing workflows?
Manufacturing workflows, in simple terms, are the step-by-step processes that guide how raw materials are transformed into finished products within a manufacturing facility.
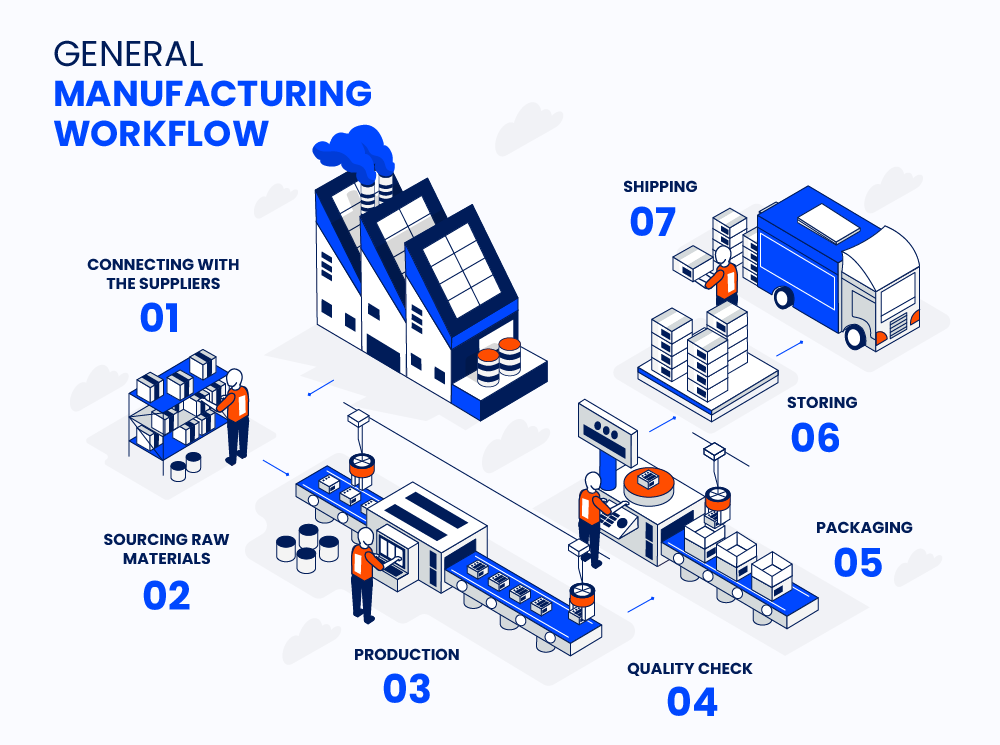
There are seven steps in a general manufacturing workflow:
- Connecting with the suppliers
- Sourcing raw materials
- Production
- Quality check
- Packaging
- Storing
- Shipping
While these are the most basic 7 steps in the workflow, there are multiple other processes involved. Let’s consider a couple of examples:
1. Assembly Line
The assembly line is a classic example of a manufacturing workflow for automotive industries. Cars move along a conveyor belt, and at each station, specific tasks are performed – adding engines, attaching wheels, installing seats, and so on. Each station represents a step in the workflow, and when everything clicks, cars roll off the line faster and more efficiently.
2. Batch Processing
In the food industry, the production of snacks like potato chips is an example of batch production. Potatoes are washed, peeled, sliced, fried, seasoned, and packaged in a specific sequence and in batches. Each of these steps is a part of the workflow, and optimizing this process ensures a consistent and cost-effective production of potato chips, or any other food items.
Understanding these examples, it’s clear that manufacturing workflows are the backbone of any company. Now, let’s explore the challenges that manufacturing companies face due to inefficient workflows.
How do inefficient manufacturing workflows impact businesses?
Here are some of the common problem statements that occur because of inefficient manufacturing workflows.
- Quality control issues
A manufacturer can lose up to 20% of revenue due to quality issues. When processes are not properly structured or monitored, it becomes challenging to maintain consistent quality standards. This can result in a higher rate of defects, increase costs owing to reworks, and potential damage to the company’s reputation.
- Resource Allocation Problems
Inefficient workflows can cause the overutilization or underutilization of some resources. For instance, some machines may be overworked, leading to breakdowns and maintenance costs, while others sit idle, wasting valuable resources. This misallocation can strain budgets and hinder overall productivity.
- Lack of agility
When workflows are rigid and resistant to change, it can be challenging to introduce new products or modify existing ones quickly. This lack of agility can result in missed opportunities and revenue loss.
- Employee frustration and burnout
Inefficient workflows can lead to employee frustration and burnout. Workers may find themselves constantly dealing with bottlenecks, delays, and repetitive tasks. Over time, this can erode morale and reduce productivity, ultimately affecting the company’s bottom line and employee retention rates.
But what causes the inefficiency in manufacturing workflows in the first place? Let’s discuss that.
Factors that lead to inefficient manufacturing workflows?
Here are the top three reasons for inefficient workflows in manufacturing:
- Lack of standardization: When each team or shift follows its own set of procedures, it can lead to confusion, inconsistency, and inefficiency. Standardization ensures that everyone is on the same page, reducing errors, and speeding up production.
- Inadequate training: If the employees are not adequately trained, they may not fully understand the best practices and nuances of their tasks. This can lead to mistakes and slower processes. Comprehensive training programs are essential to ensure that all employees have the skills and knowledge needed to perform their roles efficiently.
- Poor communication: Inefficient workflows can result from poor communication between different departments or teams within a manufacturing facility. If the information doesn’t flow smoothly between production, logistics, quality control, and other units, it can lead to delays and missed opportunities. Effective communication can increase productivity by 25%! Thus, it is crucial for streamlining workflows and maximizing efficiency.
Now that we have discussed the whys of inefficient manufacturing workflows, let’s discuss how to streamline them.
7 ways to build efficient manufacturing workflows
Here are seven ways to improve the efficiency of your manufacturing workflows to increase productivity and ensure continuous growth.
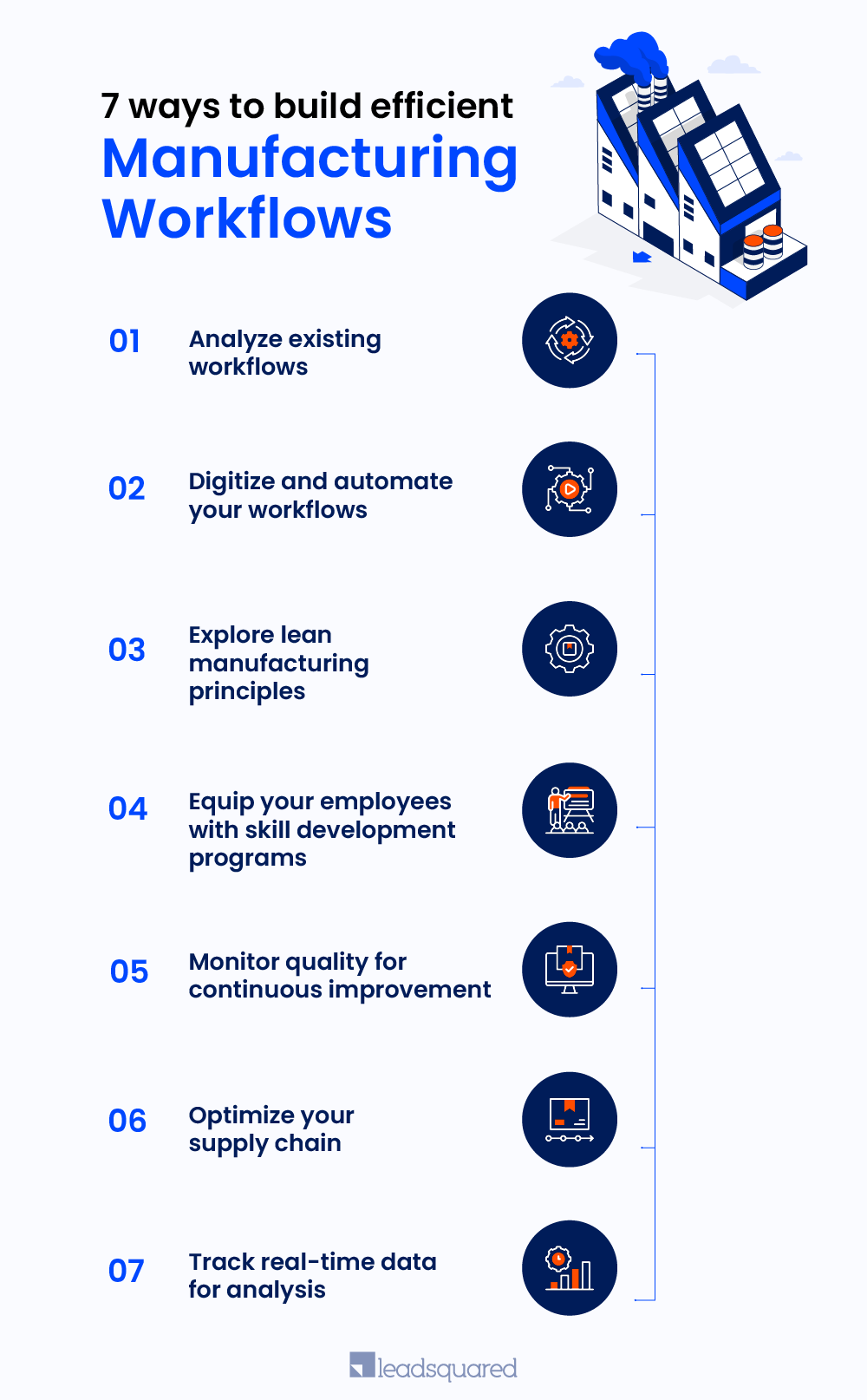
1. Analyze existing workflows
Take a close look at your current manufacturing workflows with a critical eye.
Example:
Through workflow analysis, we know that the process of testing and approving new drug formulations is unnecessarily complex and time-consuming. By re-evaluating and simplifying this workflow, you can significantly reduce the time it takes to bring new medications to market, ultimately increasing your productivity and revenue.
2. Digitization of workflows
Embrace technology by digitizing your manufacturing workflows. Implementing digital tools and software like a CRM, supply chain management, or MES solutions allows you to automate workflows and track progress in real-time to make data driven decisions.
Example:
By implementing a digital manufacturing execution system (MES), you can track the production of each garment in real-time. This system collects data on everything from fabric cutting to quality control. With this information at your fingertips, you can spot bottlenecks and make necessary changes in production to improve efficiency.
3. Lean manufacturing principles
Adopt lean manufacturing practices to eliminate waste and streamline processes.
Techniques like 5S {Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain} and Value Stream Mapping make your workflows smoother and more efficient.
Here is what 5S are:
- Sort: In this step, the goal is to separate necessary items from unnecessary ones. It involves identifying and removing any tools, materials, or equipment that are not essential for the current work process.
- Set in Order: Once you’ve sorted the essential items, the next step is to arrange them systematically. This involves designing a logical and efficient layout for tools, equipment, and materials so that they are easily accessible when needed.
- Shine: The shine step focuses on cleanliness and maintaining a tidy workplace. It includes regular cleaning and inspection of tools, machinery, and the workspace to ensure everything is in good working condition.
- Standardize: Standardization involves establishing consistent procedures and practices for maintaining the first three S’s (Sort, Set in Order, Shine). It involves creating documented processes and checklists to ensure that the workplace remains organized, clean, and efficient over time.
- Sustain: The final step, sustain, focuses on maintaining the improvements made through the previous four S’s. It involves ongoing training, regular audits, and a commitment to continuously improving the workplace.
Together, the 5S principles aim to create a workplace that is not only more organized and efficient but also safer and more conducive to productivity.
Example:
For this let’s take the example of a furniture production workshop. Applying lean principles, you decide to organize the workspace using the 5S methodology. This involves decluttering workstations, organizing tools, maintaining cleanliness, and standardizing procedures. As a result, your team can find tools and materials quickly, reduce setup times, and improve overall workflow efficiency.
4. Employee training and skill development
Invest in training and upskilling your workforce. Knowledgeable and skilled employees can perform their tasks more efficiently, reducing the chances of errors and improving the overall workflow. Well-trained teams can also adapt to changing production demands more effectively.
Example:
In an electronics manufacturing facility, investing in employee training pays off. You can provide specialized training to your assembly technicians in soldering techniques and equipment usage. With improved skills, they can solder components more accurately, leading to fewer defects and rework.
5. Quality control and continuous improvement
Implement rigorous quality control measures at various stages of your workflow to catch defects early, prevent rework, and reduce production delays. Additionally, establish a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are encouraged to suggest and implement workflow enhancements.
Example:
Suppose you operate a food processing plant. To maintain high product quality, you introduce a rigorous quality control system at various production stages. This includes visual inspections and taste tests. Feedback from these checks is used to make immediate adjustments to the process, preventing defective products from reaching consumers.
6. Supply chain optimization
Streamline your supply chain to ensure that materials and components arrive just in time for production. This reduces excess inventory, minimizes storage costs, and keeps your workflow running smoothly without interruptions caused by material shortages or overstocking.
Example:
If you manage a toy manufacturing company, optimizing your supply chain can work wonders. By establishing just-in-time inventory practices with key suppliers, you ensure that the necessary raw materials and components arrive precisely when needed. So, it is not just about adapting the tech or process, but also improving supplier relationship management.
7. Data tracking and analysis
Implement a robust data tracking and analysis system. Collect and analyze data from every stage of production, from component assembly to quality control checks, to identify patterns and trends.
Example:
Let’s say you start tracking product quality of all suppliers and generate a report regularly. Now you can easily notice if a specific supplier consistently delivers faulty components. Armed with this information, you can take corrective actions such as switching suppliers or tightening quality control measures. This helps you to improve product quality and reduce costs associated with defects.
By combining these strategies, you can transform your manufacturing workflows into well-oiled machines and drive productivity up and costs down.
Now, these tips can boost your manufacturing efficiency and output. But remember, a company’s success isn’t just about what it makes; it’s about what it sells. To up your manufacturing sales, prioritize your team’s productivity and efficiency.
How to improve team productivity and efficiency?
1. Focus on employee training and development
In a survey 74% of employees said they feel they aren’t reaching their full potential at work due to a lack of development opportunities. Employee training can play a pivotal role in fostering a skilled and adaptable workforce.
By offering comprehensive skill enhancement programs, continuous learning opportunities, and hands-on experience, manufacturers empower their employees with the knowledge and expertise needed to excel in their roles. Cross-training initiatives further enhance versatility, ensuring that employees can seamlessly switch between tasks when necessary.
2. Automate your sales and marketing efforts with a manufacturing CRM
A manufacturing CRM helps you streamline and increase efficiency of your sales, marketing and dealer management. It helps you:
- Map your entire partner ecosystem (dealers, distributors and influencers) on one platform.
- Track activities of your field sales team in real-time with the mobile app.
- Personalize and automate communication to boost partner relationship, upsell, and cross-sell.
- Generate real-time reports across zones, territories, regions and hierarchies.
- Track performance, KPIs, and goal regularly with reports and dashboards.
To know about how a manufacturing CRM can increase productivity across teams, book a personalized demo today.
And that’s a wrap
So, here’s the deal – manufacturing workflows? They’re your company’s bread and butter. We’ve talked about the challenges related to manufacturing workflows and what causes them. We also looked into some tested methods to improve the efficiency of your workflows. So, remember, in this fast-paced manufacturing world, optimizing your workflows isn’t just a suggestion; it’s how you can stay ahead of the curve and thrive in the game.
FAQs
There are multiple types of manufacturing workflows, some of which are: Continuous flow manufacturing, Job shop manufacturing, Lean manufacturing, Batch manufacturing, and Assembly line manufacturing.
In a push manufacturing workflow, production is driven by a predetermined production schedule, often based on forecasts or sales predictions. Whereas in a pull manufacturing workflow, production is initiated in response to actual customer demand.
The five basic steps of a manufacturing workflow are:
1. Capture: Gathering and recording information or inputs required for the workflow.
2. Processing: Analyzing, organizing, or transforming the captured data or materials.
3. Routing: Determining the path or sequence for the data or materials to follow.
4. Approval: Obtaining necessary authorizations or decisions at various stages of the workflow.
5. Completion: Finalizing the workflow by delivering the end result or output, which may involve archiving or further actions.