Imagine you need to extract solutions from hundreds of pages of data within 5 minutes. Seems impossible, right? But this is just another day in a healthcare provider’s life.
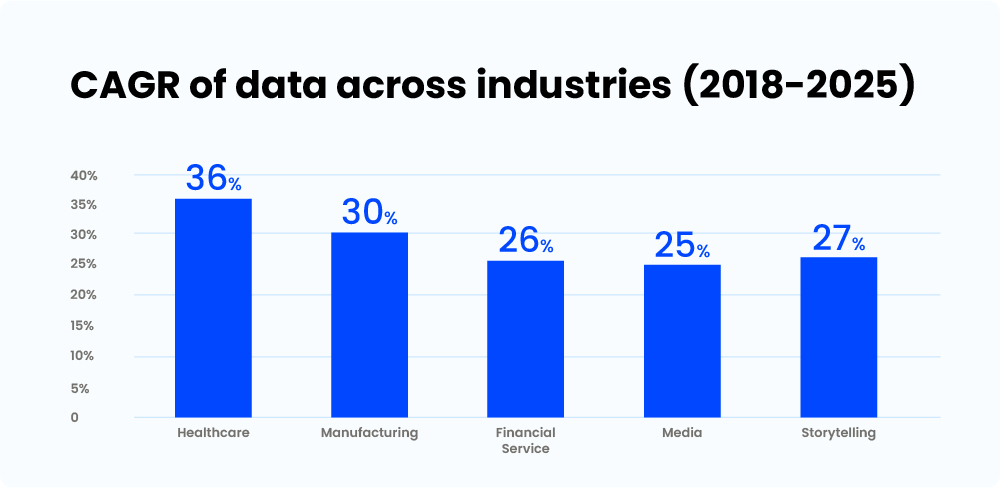
The healthcare industry is full of medical data. Today, 30% of the global data generated is from the healthcare industry, and it is estimated to reach 36% by 2025. Now, this may not look like tremendous growth, but it is 11% faster than the entertainment industry and 10% than the finance sector.
Generating and maintaining medical data is essential to improve the overall quality of care at hospitals and other healthcare facilities. But doctors spend 18.5 million hours a year completing these administrative tasks in the form of data collection.
At the same time, your patients expect better customer service, safety, and the option to have all medical records at their fingertips.
So, what’s the solution to the three-pronged challenge of meeting patient expectations, improving the quality of care, and reducing the burden on healthcare providers?
Interoperability!
In this article, we will discuss the importance of interoperability in healthcare, its benefits, and how you can achieve it for your healthcare organization.
First, let’s understand what it means.
What is Interoperability in Healthcare?
Interoperability in healthcare is the ability of different healthcare information technologies (HIT) to exchange, comprehend, and use data effectively. It improves patient outcomes and the quality of care delivered at a healthcare facility. Healthcare Information Exchange (HIE) electronically enables the transfer of data among these systems.
Interoperability is not limited to connecting EHR or EMRs. You can also integrate your systems across other medical software used by different departments or teams.
For example, integrating your EHR with a Healthcare CRM, to streamline the flow of patient information captured while booking an appointment.
To understand interoperability better, let’s dive into a world with complete interoperability.
Example of Interoperability in Healthcare
Imagine, a patient suffers from a fever and visits a general physician.
Since the state has complete interoperability, the doctor can see the patient’s entire medical history and the treatments they have undergone at other healthcare facilities. He also has access to minor details like the duration of the treatments and the medication prescribed.
He notices a pattern and advises the patient to consult a specialist.
When the patient reaches the hospital, they don’t have to carry any files, fill any forms, or even wait in line. The referral has already been shared by the general physician with the complete patient profile.
The specialist sees the patient and sends his profile for lab tests. The lab sends a notification with the slot to submit samples. Once the reports are ready, they are shared with the doctor and patient digitally.
The billing counter generates the patient’s bill with just one click. The system also verifies if there is insurance coverage and claims the bill with the insurance provider.
In this complete patient journey, interoperability:
- Eliminates the need to record patient information at multiple stages.
- It saves the patient’s and the healthcare provider’s time.
- It also keeps the patient and doctor updated on the lab’s progress.
- Overall, it improves the quality of care and patient experience.
This incident is just one of the examples of the healthcare data exchange between an individual and an organization. A few other examples include:
- Patients communicating through chat, emails, or any other application with the organization.
- An organization records or shares data through EHRs.
- Patients looking up healthcare services like insurance, treatments, etc., online.
- An individual receiving notifications from an organization about follow-ups or lab results.
There are many more use cases where the information is shared at a larger scale, and this is why it is important to have a seamless process for the same.
Before we discuss interoperability in detail, let’s understand what health information exchange is, and how it enables a smooth flow of data.
What is Health Information Exchange (HIE)?
Health information exchange, or HIE, enables the flow of medical data electronically within HIE systems. It helps in easy access and retrieval of medical data to provide safe, quick, efficient, and patient-centered care.
Various healthcare and HIE organizations in the United States provide software and services to facilitate HIE. They also promote the sharing of information electronically with medical associations.
Data sharing happens at different levels. It takes place between individuals, systems, organizations, and even states.
Next, we’ll take a look at the different levels of interoperability in healthcare.
Different Levels of Interoperability in Healthcare
According to an article by Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS), there are four different levels of interoperability.
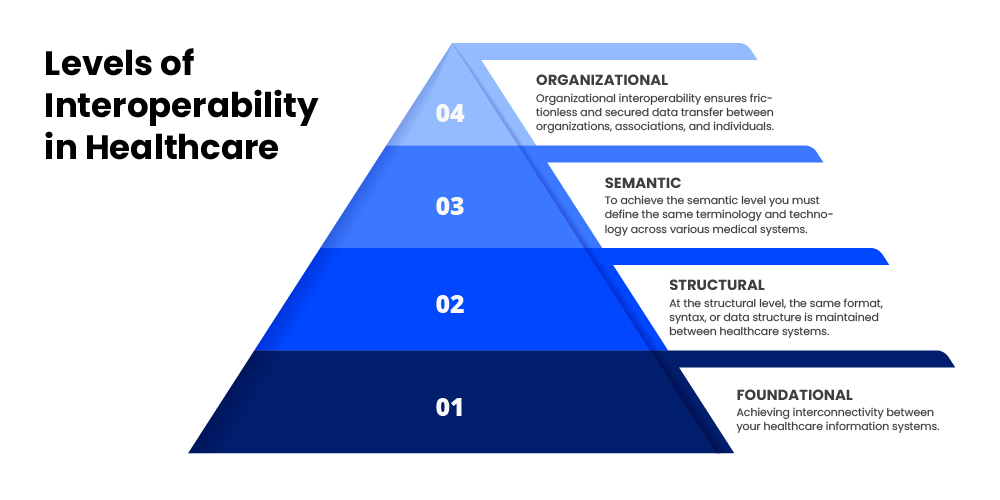
Level 1: Foundational
Achieving interconnectivity between your healthcare information systems is the foundation level. The aim here is to transfer data from one healthcare system or department to another seamlessly. The receiver should obtain the exact medical data instead of its interpretation. It is generally the least complex process.
Level 2: Structural
The structural level focuses on maintaining the same format, syntax, or data structure between systems like EHR, HMS, billing software, monitoring devices, appointment booking application, and more. This standardization helps in interpreting data at the field level, e.g., patient records. It is a more complex process since it requires users to define the data structure. While the data captured is in the same format at this level, the extent to which you can use it is still limited.
Level 3: Semantic
Once you have built your foundation and achieved interpretation ability at the receiver end, the next step is to use the data to its maximum potential. To achieve this, you must remove the gaps by defining the same terminology and technology across various medical systems.
An organization generally implements interoperability till the 2nd or 3rd level. As these levels meet the primary goal of making data accessible to everyone in the healthcare organization. But, to have interoperability at the population level, you need organizational interoperability.
Level 4: Organizational
Organizational interoperability includes all governance, policy, social, legal, and administrative considerations. It ensures frictionless and secured data transfer between organizations, associations, and individuals.
All the different levels and complexity may be a little overwhelming. So, here are a few steps to help you achieve interoperability in your healthcare organization.
5 Steps to Achieve Interoperability for Your Healthcare Information Systems
1) Set a goal
Starting without setting a goal is like walking on a road without signs!
You can set a goal according to the level of interoperability and the timeline within which you want to achieve that. If your healthcare facility has already achieved a certain level of interoperability, look for possibilities to level up. You can also set a goal to include multiple departments within your hospital.
For beginners, to achieve interoperability in your organization till level 2 or 3, start with building a plan. Set goals and timelines for each step. Include everything, like human resources, software, or implementation of any technology. Consider partnering with an external vendor if required.
As this process will involve exchanging critical patient information, it is important to ensure the data is protected and transferred safely. Different healthcare regulations and compliances like HIPAA helps organizations to build secure systems and processes. So, make these compliances are followed by internal and external teams (if any).
[Also read: A 12 Rule HIPAA Compliance Checklist to Guide You in 2023]
Once you have the plan and goals in place, look for the possibility of achieving interoperability with your existing system. If feasible, it will be a quick and cost-effective solution.
2) Analyze your existing system
Before jumping into the process:
- Sit back for a minute and analyze your current data-sharing process. If you already use an EHR or HIE, check if you can expand them and create interoperability within the existing systems.
- Do a thorough technical analysis of all the software and understand your desired level.
- If required, take an expert opinion.
If you are still using the restricted, slow, and unsecure pen-paper method to capture and share information even in a single department, implementing an EHR would be the first step. Ensure the adoption of EHR by each department or individual to share information across systems like appointment booking, billing, etc.
3) Ensure adoption of the standards
The next step would be to define the data format and technology standards. It is essential that you use the same technology for all the software and applications implemented. This standardization will ensure that systems can also analyze the shared data. You can adopt an FHIR for this process.
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) is an open-source standards framework for healthcare data. It simplifies the transfer of healthcare data between systems.
It provides a standardized framework to organize and utilize data using various computer systems or applications. FHIR groups data into resources like patients, conditions, and medications.
Financial and workflow data, such as details about claims, meetings, and more, can also be structured using FHIR.
At the same time, standardizing the organization’s terminology makes it easy for everyone to comprehend and interpret the data. To help you with this, the World Health Organization created the ICD-10 medical classification system. It includes codes for signs and symptoms, diseases, abnormal findings, complaints, external causes of injury or conditions, and social factors.
4) Privacy and security
Patient healthcare information is sensitive data that patients share with trusted organizations. To protect and keep the data secure, follow data exchange laws like HIPAA. Ensure all your systems comply with HIPAA and conduct training sessions for your staff and physicians.
5) Build a seamless end-to-end patient journey
Remember, one of the reasons why we are creating interoperability is to improve the patient experience. And patient experience starts from the first touch point, which can be anything from booking an appointment or even before that.
So, to improve the experience, you also need to understand patient behavior at each level.
A HIPAA-compliant healthcare CRM helps you record patient interactions at different touch points and presents them as easy-to-read reports or healthcare dashboards. While an EHR only records the data once the patient completes the appointment, a healthcare CRM gives you an end-to-end visibility of patient’s journey.
So, to create a seamless patient journey, integrate your CRM with the EHR and transfer the data captured from CRM from day one to get a holistic view of patient data and interactions.
Benefits of Interoperability in Healthcare
Let’s look at some primary benefits you will observe after achieving interoperability in your healthcare system.
1. Reduced medical errors and improved efficiency
A John Hopkins study claimed that medical errors cause deaths for more than 250,000 people in the US annually. After heart disease and cancer, it is the third leading cause of death.
Interoperability helps you eradicate manual data entry—that’s generally laden with human errors—and reduce the chances of medical errors while improving staff efficiency.
2. Improved patient experience and care
In a study, 92% of physicians in the US believed that interoperability could improve patient experience. Eliminating manual entry of records saves time so physicians can spend more time with patients which positively impacts patient satisfaction. At the same time, with easy data access, physicians can provide quick and more accurate diagnoses.
3. Stronger privacy and security for patients
Patient medical data is sensitive information and with interoperability in place, you can restrict data access to only authorized personnel. Cyberattacks are another threat to data security. However, by ensuring HIPAA compliance in your system, you can ensure data is shared safely and securely with the staff and physicians.
4. Reduced healthcare costs
Research showed that interoperability between EHR and medical devices in the US healthcare could save them $30 billion annually. Interoperability streamlines care delivery and improves the organization’s finances. Automating healthcare workflows and information transfer allows healthcare providers to care for more patients.
You can increase the list of your benefits by including a healthcare CRM. Here is how it helps in the process of building interoperability.
How can a healthcare CRM help you achieve complete interoperability in healthcare?
The whole idea of building interoperability in healthcare is to connect the systems for a smooth flow of information for better healthcare outcomes.
A healthcare CRM helps in this process by connecting patient interactions with an organization to the EHR or EMR. It captures the interactions from all the sources like websites, mobile apps, messengers, or call centers to store data like appointment booking, lab results, etc. It notifies all the stakeholders about any progress or activity on the patient profiles.
A CRM also prevents the duplication of data by maintaining a single patient profile and updating the same when required. Choosing the right Healthcare CRM can save a lot of time for your business and streamline the process to improve efficiency.
For example: Manipal Hospitals improved team collaboration and patient management by integrating LeadSquared healthcare CRM with their HIS.
LeadSquared’s APIs and connectors help us collect detailed patient data and integrate it with our core HIS system. The dashboards and reports enable us to work with this data and derive great insights from it. Both these features help streamline processes, save time, and in turn boost team productivity.
Kiran Ramakrishna, Assistant Manager, Manipal Hospital
To wrap it up
Interoperability between EHR systems powered by HIE would make healthcare data universally sharable, facilitate patient care and allow seamless referrals and transitions between healthcare providers.
Moreover, combining a CRM with your EHR creates interoperability from the first point of contact with the patient. It improves communication and data sharing between the patient and healthcare provider. Overall, it will enable you to provide better patient experience and healthcare outcomes.
Get in touch with our team to know how LeadSquared can integrate with your existing system and improve patient management.